Archive: 2026/02

- 11 Comments
Generic drugs must meet the same FDA standards as brand-name drugs, including pharmaceutical and bioequivalence. Learn how testing, manufacturing rules, and inspections ensure quality and safety.

- 14 Comments
Not all severe drug reactions mean you need to avoid entire medication families. Learn which reactions require strict avoidance and which don’t, and how to avoid unnecessary drug restrictions that limit your treatment options.

- 14 Comments
Every part of your prescription label has a purpose - from your name to the expiration date. Understanding what each section means can prevent dangerous mistakes and help you take your medicine safely.

- 10 Comments
Authorized generics let brand drugmakers launch their own low-cost versions during generic exclusivity, undercutting independent competitors and slowing price drops. This legal but controversial tactic distorts competition and keeps drug prices higher than they should be.

- 16 Comments
Learn how to safely check supplement-drug interactions using verified databases like NatMed. Step-by-step guide for clinicians to prevent dangerous adverse events and improve patient safety.
- 8 Comments
The time you take your medication can reduce side effects and boost effectiveness. Learn how chronotherapy uses your body’s natural rhythms to make drugs safer and more powerful.

- 10 Comments
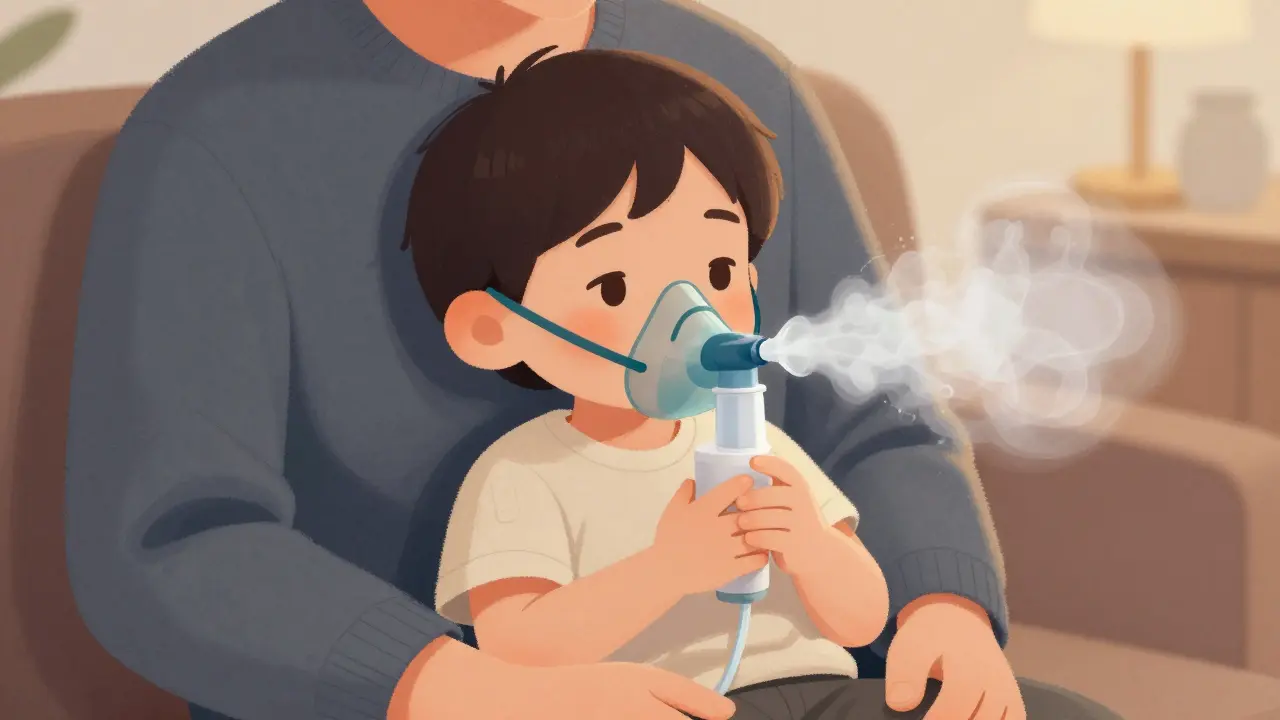
Nebulizers and inhalers both deliver asthma and COPD medication, but which one works best? Evidence shows inhalers with spacers are faster, cheaper, and just as effective for most people - except young children and those who can't coordinate breathing.

- 15 Comments
Chronic eczema is caused by a broken skin barrier, not just allergies or stress. Learn how to repair it with ceramide creams, avoid common triggers, and stop the itch without relying on steroids. Real science, real results.

- 9 Comments
The Hatch-Waxman Act of 1984 balanced drug innovation and generic access. It created the ANDA pathway, patent term restoration, and Paragraph IV challenges. Today, generics make up 90% of prescriptions but only 18% of spending. Learn how this law works and its ongoing challenges.

- 14 Comments
Antipsychotic medications carry serious metabolic risks including weight gain, diabetes, and heart disease. This article explains the differences between drugs, why regular monitoring is critical, and practical steps for patients and doctors to prevent life-threatening complications.
