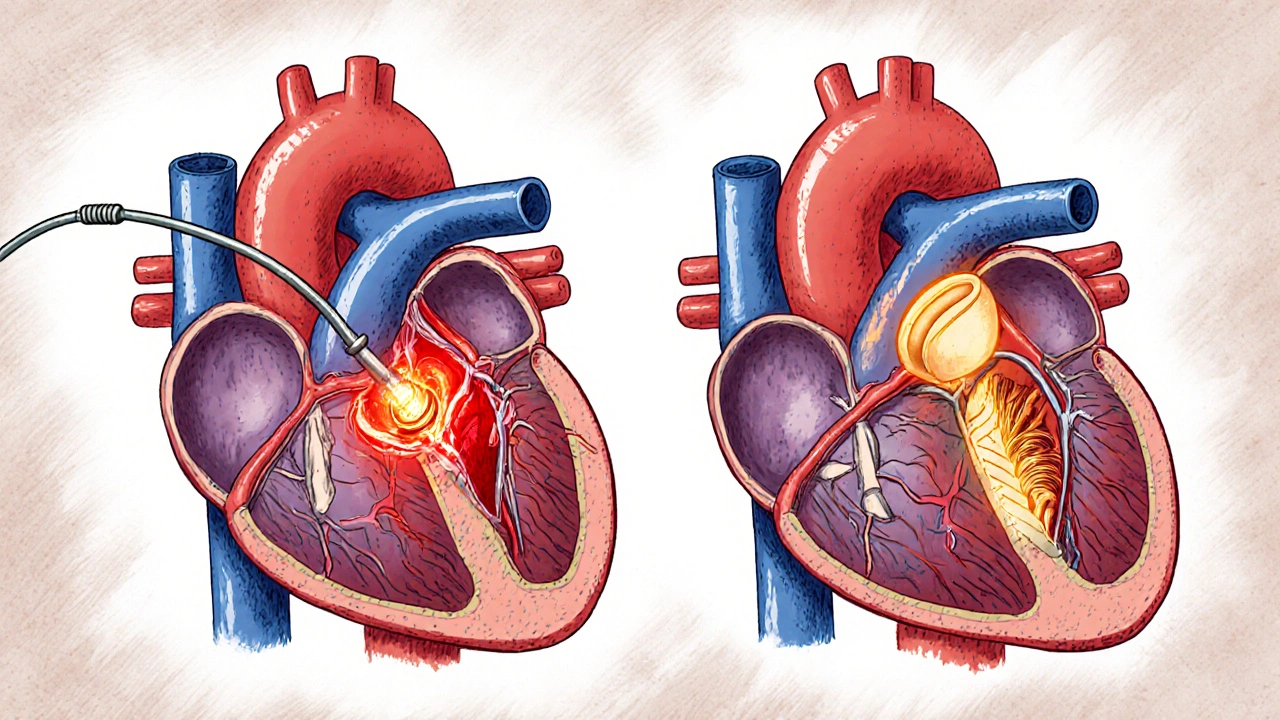
PCI vs CABG: Understanding Heart Revascularization Options
When arteries supplying the heart become severely blocked, two main procedures can restore blood flow: percutaneous coronary intervention, a minimally invasive procedure where a balloon and stent are used to open blocked arteries. Also known as angioplasty, it's often done as an outpatient procedure with quick recovery. The other option is coronary artery bypass grafting, a surgical procedure where a blood vessel from another part of the body is used to route blood around a blocked artery. These aren’t just technical choices—they directly affect how long you live, how well you feel, and what your daily life looks like after treatment.
PCI is faster, less invasive, and usually gets you home the same day. But if you have multiple blockages, diabetes, or weakened heart muscle, CABG often gives better long-term results. Studies show that for people with three-vessel disease, CABG reduces the chance of needing another procedure by nearly half over five years compared to PCI. It’s not about which is "better"—it’s about which fits your body, your health history, and your goals. For example, if you’re young and active, avoiding repeat procedures matters. If you’re older with other health issues, avoiding major surgery might be the priority.
Both procedures carry risks. PCI can lead to stent re-narrowing or blood clots, requiring long-term antiplatelet drugs. CABG involves open-heart surgery, so infection, stroke, and longer recovery are real concerns. But neither is a cure—both are tools to manage disease. Lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and regular monitoring still matter more than the procedure itself. Your doctor will look at your angiogram, check your kidney function, assess your diabetes control, and weigh your age and activity level before recommending one over the other.
What you’ll find in the posts below are real-world comparisons, patient stories, and medical insights that cut through the noise. You’ll see how drugs like amiodarone and NSAIDs interact with heart treatments, how generic alternatives affect cost and access, and why medication safety becomes even more critical after either procedure. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or just trying to understand your options, this collection gives you the facts you need—not the marketing.
- 14 Comments
PCI and CABG are the two main treatments for blocked heart arteries. Learn how they differ, which is better for diabetes or complex disease, and how doctors decide between stents and bypass surgery using real-world data.
