CABG Surgery: What You Need to Know About Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
When your heart’s arteries get clogged, CABG surgery, a procedure that reroutes blood around blocked coronary arteries using a healthy vessel from another part of the body. Also known as coronary artery bypass grafting, it’s one of the most common heart surgeries in the U.S. and can mean the difference between ongoing chest pain and a return to normal life. It’s not a cure for heart disease, but it’s a powerful tool to give your heart the blood it needs.
CABG surgery is often recommended when medications and lifestyle changes aren’t enough, especially if multiple arteries are blocked or the left main artery is affected. It’s not just for older adults—people in their 40s and 50s with severe blockages due to diabetes, high cholesterol, or smoking can need it too. The surgery uses a vein from the leg, an artery from the chest, or sometimes the arm to create a new path for blood. Each graft acts like a detour around the blockage, letting oxygen-rich blood reach the heart muscle again. This isn’t a quick fix; it’s a long-term solution that often comes with major lifestyle changes afterward.
Recovery takes time. Most people stay in the hospital for about a week, then spend weeks healing at home. Physical therapy and cardiac rehab are often part of the plan—not just to get stronger, but to learn how to avoid another blockage. Many patients wonder if they’ll ever feel like themselves again. The answer is yes, but it takes patience. The real success of CABG isn’t just the surgery itself—it’s what happens after. Managing blood pressure, quitting smoking, sticking to a heart-healthy diet, and taking prescribed meds like statins or blood thinners are just as important as the operation.
Not everyone needs bypass surgery. Some people do better with stents, especially if only one or two arteries are narrowed. But when the blockages are complex or widespread, CABG is often the best choice. Doctors look at the pattern of blockages, your age, other health issues like diabetes, and how much your heart is already damaged. It’s not a one-size-fits-all decision.
You’ll find posts here that dig into the details: how CABG relates to other heart treatments, what medications are used before and after, how to spot complications early, and what recovery really looks like for real people. There’s also info on how to reduce risks, what to ask your surgeon, and how to tell if your symptoms are normal or something to worry about. These aren’t just medical guides—they’re practical checklists, warning signs, and lived experiences from people who’ve been through it. Whether you’re a patient, a caregiver, or just trying to understand what CABG means for someone you love, this collection gives you the facts without the fluff.
- 14 Comments
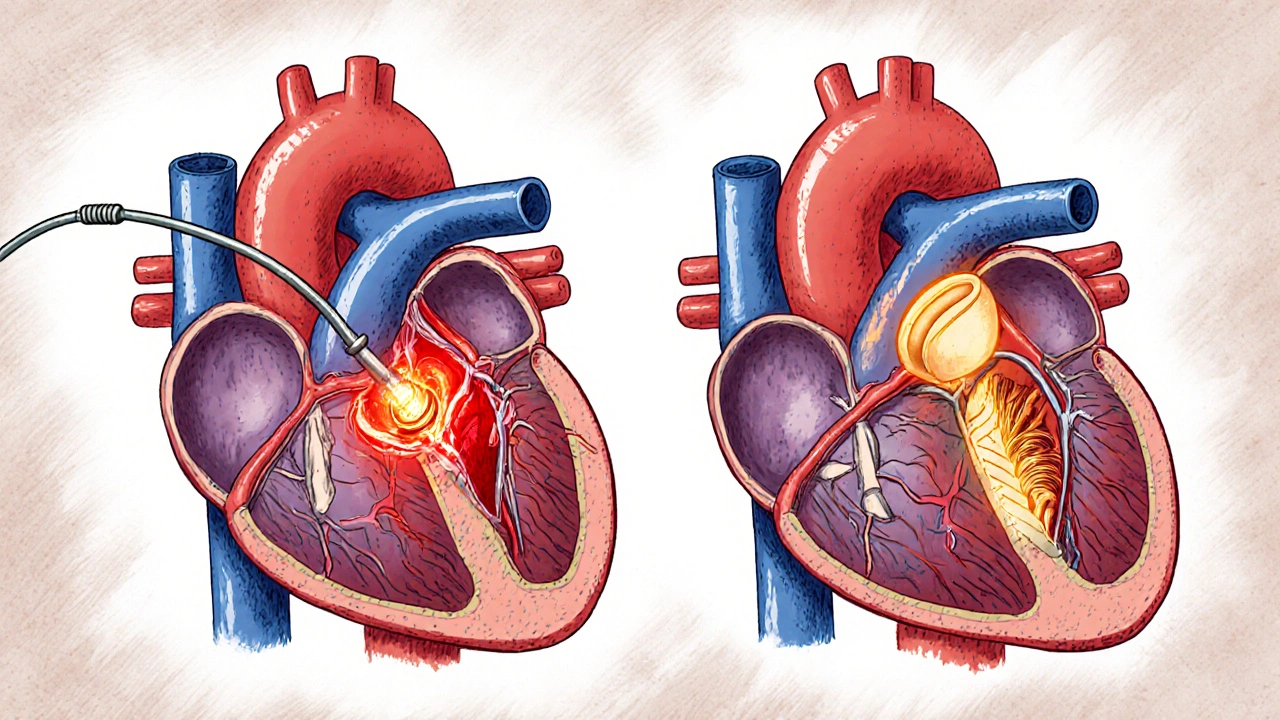
PCI and CABG are the two main treatments for blocked heart arteries. Learn how they differ, which is better for diabetes or complex disease, and how doctors decide between stents and bypass surgery using real-world data.
