Amiodarone: Uses, Risks, and What You Need to Know
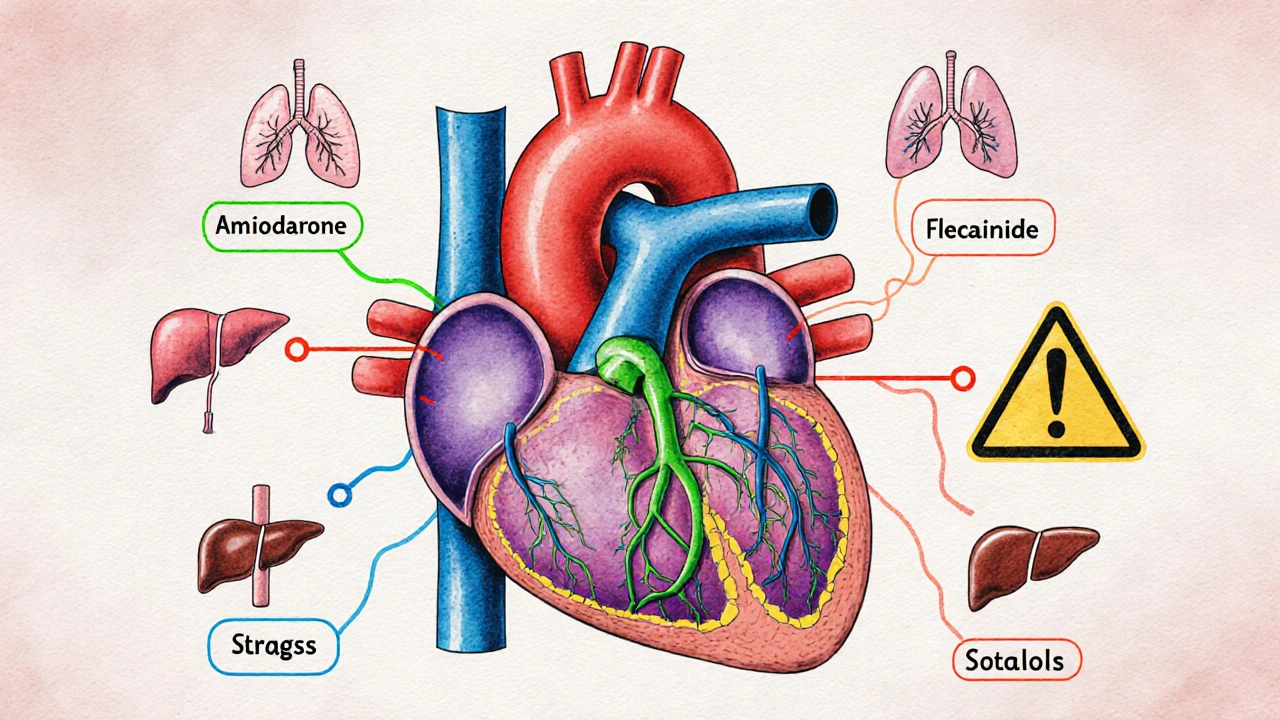
When your heart doesn’t beat right, amiodarone, a potent antiarrhythmic drug used to treat life-threatening irregular heartbeats. Also known as Cordarone, it’s one of the few medications that can reset a dangerously fast or chaotic heart rhythm—but it’s not a gentle fix. Unlike most heart drugs, amiodarone sticks around in your body for weeks, even months, after you stop taking it. That’s why doctors only prescribe it when other treatments have failed or when the risk of sudden cardiac arrest is high.
It’s not just about the heart. amiodarone, a thyroid-altering medication with wide-ranging systemic effects can mess with your lungs, liver, eyes, and skin. People on long-term amiodarone often need regular blood tests, chest X-rays, and eye exams just to catch problems early. Some develop a blue-gray tint to their skin, others get a cough that won’t quit—signs it might be damaging the lungs. And because it interacts with so many other drugs, including statins, blood thinners, and even some antibiotics, your pharmacist needs to know everything you’re taking.
There’s a reason you won’t find amiodarone in most over-the-counter supplement stacks. It’s a hospital-grade tool, not a daily maintenance pill. That’s why compounded medications, custom formulations made by specialty pharmacies when standard doses don’t fit a patient’s needs sometimes come into play. If you need a lower dose, a liquid form, or a version without certain fillers, a compounding pharmacy might be your only option. But even then, you still need close monitoring. No shortcut replaces the need for regular check-ins with your cardiologist.
Amiodarone isn’t the only tool for heart rhythm problems, but it’s one of the few that works when everything else fails. Still, it’s a trade-off: control over a dangerous arrhythmia, at the cost of potential long-term damage. That’s why knowing the signs of trouble—like unexplained fatigue, shortness of breath, or changes in vision—isn’t optional. It’s survival.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides on how amiodarone fits into broader medication safety, what to watch for when mixing it with other drugs, and how personalized dosing through compounding can make a difference. These aren’t theoretical discussions—they’re what patients and pharmacists actually deal with when this drug enters the picture.
- 11 Comments
Amiodarone is highly effective for dangerous heart rhythms but carries serious long-term risks. Learn how it compares to other antiarrhythmic drugs, when it's truly needed, and safer alternatives that may work better.
